Tea, a beverage cherished for centuries across various cultures, has not only been a source of comfort but has also exhibited numerous health benefits.
In recent times, as the world faces challenges in combating infectious diseases, there has been a growing interest in exploring the potential of natural remedies.
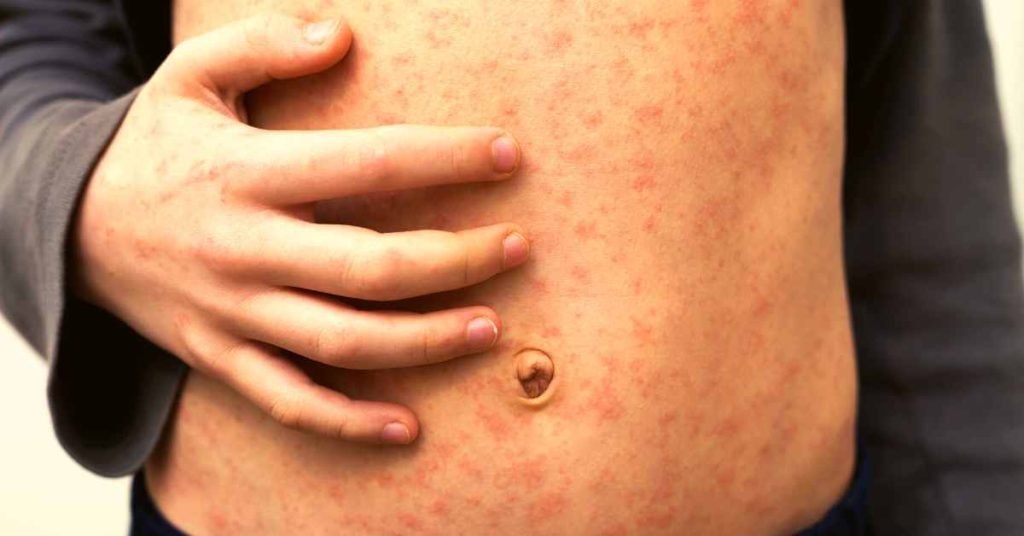
One such avenue of investigation involves the role of tea in managing measles, a highly contagious viral infection.
Measles Overview
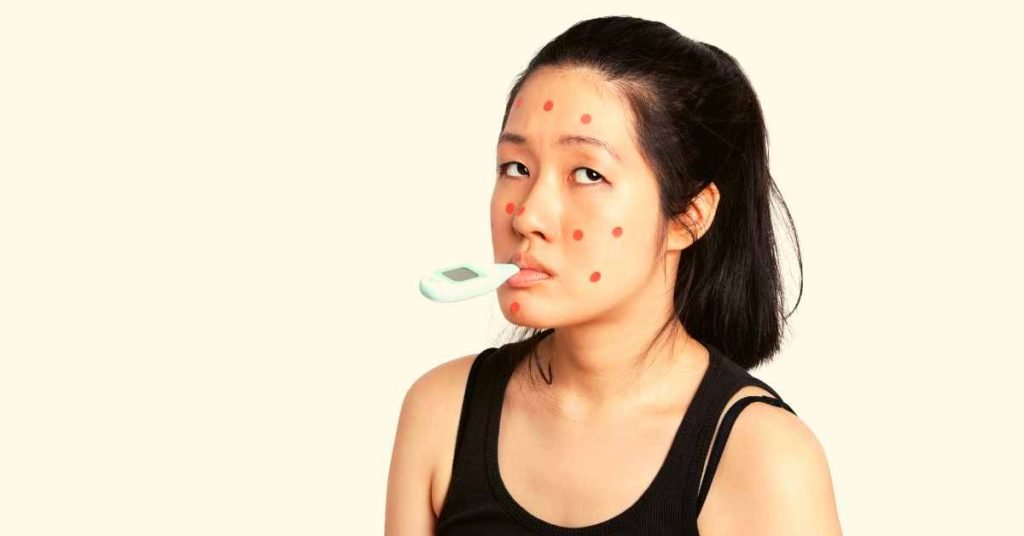
Measles, caused by the measles virus, is characterized by fever, cough, runny nose, and a distinctive red rash.
Although vaccination programs have significantly reduced the prevalence of measles, outbreaks still occur, and the disease poses a serious threat to public health.
While vaccination remains the primary prevention strategy, the complementary use of natural remedies, such as tea, has been gaining attention for its potential supportive role.
Tea and Its Therapeutic Properties
Tea, derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, contains a rich assortment of bioactive compounds with known health benefits.
These include polyphenols, catechins, and flavonoids, which exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral properties.
Additionally, the diverse range of herbal teas, such as chamomile, ginger, and echinacea, further extends the therapeutic potential of tea in managing various health conditions.
Antioxidant Defense Against Measles

The pathogenesis of measles involves oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to the severity of symptoms. Tea’s high antioxidant content can counteract oxidative damage by neutralizing free radicals.
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a potent catechin found in green tea, has demonstrated antiviral properties against various viruses, suggesting its potential efficacy in combating the measles virus.
Immune-Modulating Effects
Tea’s impact on the immune system is multifaceted. The polyphenols in tea have been shown to modulate immune responses, enhancing the activity of immune cells.
This immune-boosting effect may aid in the body’s ability to mount a robust defense against the measles virus, potentially reducing the duration and severity of the infection.
Anti-Inflammatory Action
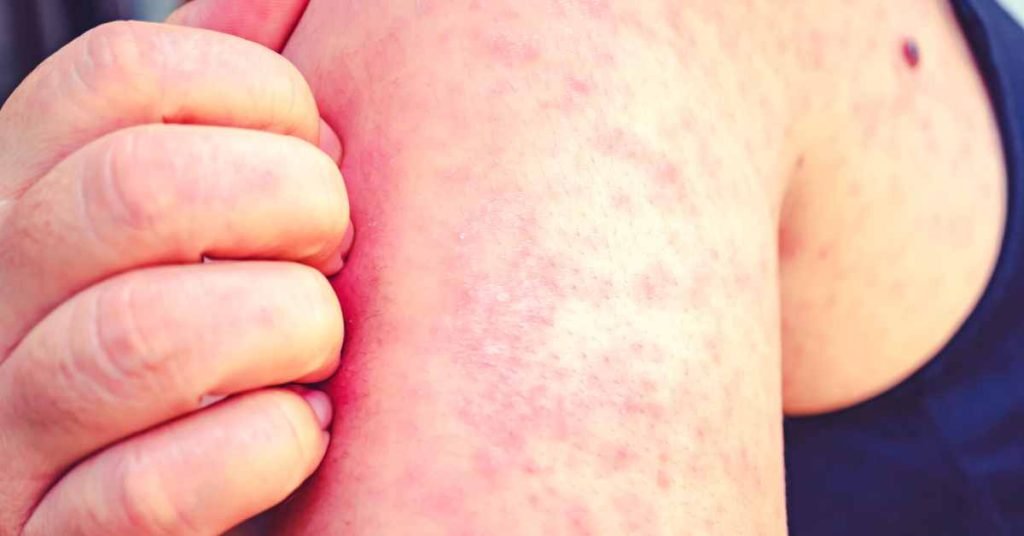
Measles often triggers an inflammatory response in the body, leading to symptoms such as fever and respiratory distress.
Tea’s anti-inflammatory properties, attributed to compounds like theaflavins and catechins, can help alleviate these symptoms and contribute to the overall comfort of individuals affected by measles.
Herbal Teas and Measles Management
Beyond traditional teas, herbal infusions have been explored for their potential in managing measles symptoms. Chamomile tea, known for its calming and anti-inflammatory properties, may provide relief from fever and discomfort.
Ginger tea, with its anti-nausea and immune-boosting effects, could aid in managing gastrointestinal symptoms associated with measles.
Caution and Considerations
While the potential benefits of tea in managing measles are intriguing, it is essential to approach such remedies with caution.

Tea should not be considered a substitute for medical treatment, and individuals with measles should seek professional healthcare guidance.
Moreover, the appropriateness of specific teas may vary depending on an individual’s health status, allergies, and existing medications.
Final Word
Tea, with its rich history as a beverage and a source of health-promoting compounds, holds promise in supporting the management of measles.
The antioxidant, immune-modulating, and anti-inflammatory properties of tea and herbal infusions may offer relief from symptoms and contribute to the overall well-being of individuals affected by measles.
However, it is crucial to integrate tea-based remedies as part of a comprehensive healthcare approach and under the guidance of medical professionals.
As research in this area continues, the potential synergy between traditional medicine and natural remedies may unveil new avenues for managing infectious diseases like measles.
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
Itsnevernotteatime.com cannot and does not contain medical/health advice. The medical/health information is provided for general and educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional advice.