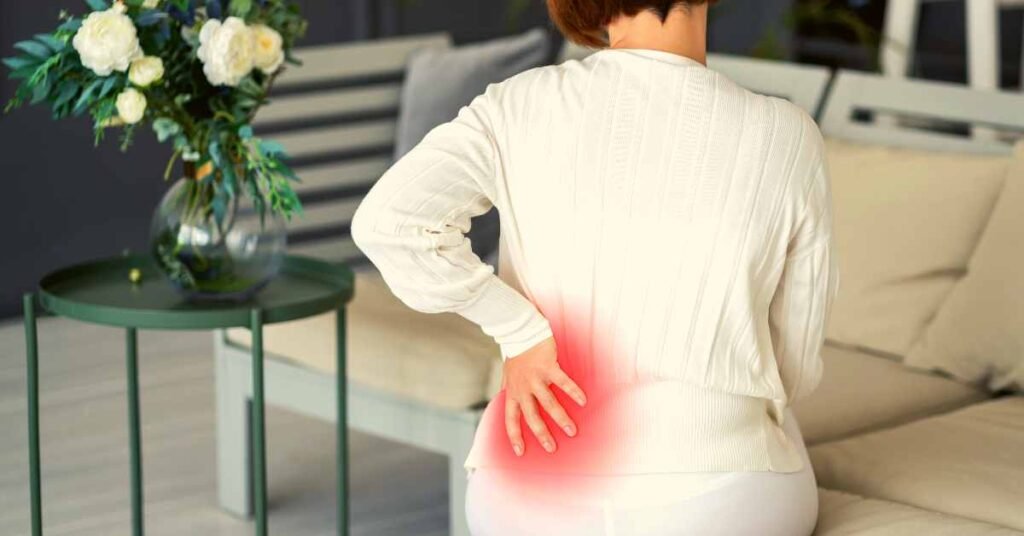
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine, causing pain, and stiffness, and potentially leading to fusion of the vertebrae.
Managing AS involves a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential benefits of incorporating tea into the management of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
This article explores the various types of tea and their potential impact on AS symptoms.
Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis
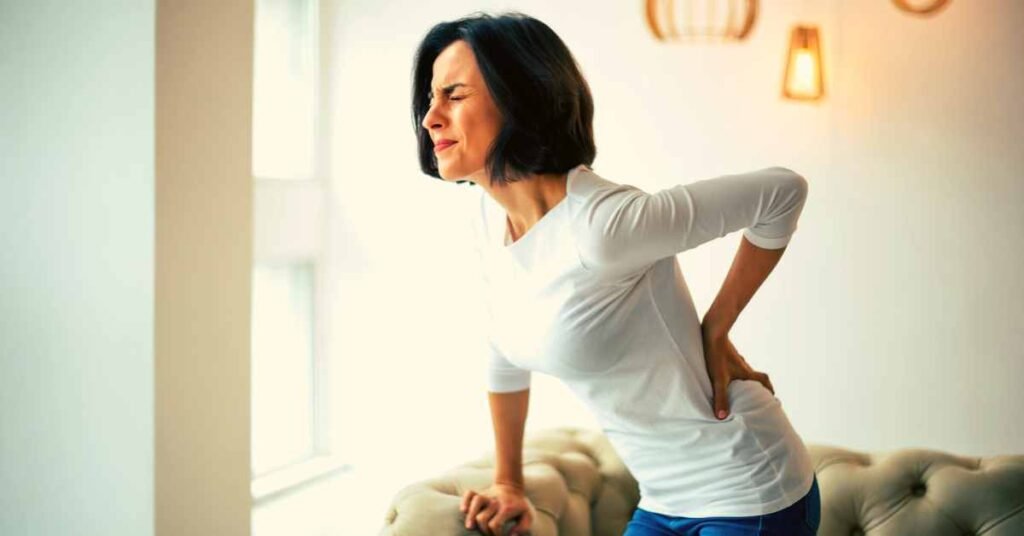

Before delving into the benefits of tea, it’s crucial to understand the nature of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
This autoimmune disorder primarily targets the spine, causing inflammation that can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility.
Over time, the inflammation may lead to the fusion of the spinal vertebrae, resulting in a hunched-forward posture.
While there is no cure for AS, various treatments aim to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Tea
Tea, a beverage enjoyed by many around the world, comes in various forms, each with its unique set of health benefits.
One notable feature of certain teas is their anti-inflammatory properties. Green tea, for example, contains polyphenols, particularly catechins, which have been studied for their anti-inflammatory effects.
These compounds may help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially offering relief to individuals with inflammatory conditions like AS.
Green Tea and Its Potential Impact on AS
Green tea has gained recognition for its potential role in managing inflammatory conditions.
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a powerful antioxidant found in green tea, has been shown to modulate the immune response and exhibit anti-inflammatory effects.

While research specifically on AS and green tea is limited, the general anti-inflammatory properties of green tea suggest that it could be a valuable addition to the lifestyle of those living with AS.
Herbal Teas for Pain Relief
Beyond green tea, various herbal teas are celebrated for their pain-relieving properties.
Ginger tea, for instance, has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects that may provide relief to individuals dealing with AS-related pain.
Turmeric tea, derived from the turmeric root, contains curcumin, a compound known for its potent anti-inflammatory properties.
Incorporating these herbal teas into a daily routine may contribute to managing pain associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis.
The Role of Hydration in AS Management
Proper hydration is essential for individuals with AS, as it helps maintain joint function and flexibility.
Tea, whether herbal or traditional, contributes to daily fluid intake. Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health and can positively impact joint mobility.
Additionally, warm beverages like tea may offer comfort to those experiencing stiffness, a common symptom of AS.
Caffeine and AS
While some teas, such as green tea, contain caffeine, it’s essential to consider its potential impact on AS symptoms.
Caffeine can act as a stimulant and may affect sleep patterns, which is particularly relevant for individuals with AS who may already experience sleep disturbances.
Individuals with AS should monitor their caffeine intake and assess how it may influence their symptoms.
Mind-Body Connection: The Ritual of Tea
Beyond the physical benefits, the act of preparing and savoring a cup of tea can have positive effects on mental well-being.
The ritual of tea can provide a moment of calm and relaxation, which is valuable for individuals managing a chronic condition like AS.
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate symptoms, and incorporating mindfulness practices, such as enjoying a cup of tea, may contribute to an overall sense of well-being.
Potential Considerations and Individual Variability

While tea, especially varieties with anti-inflammatory properties, may offer benefits to some individuals with AS, it is crucial to recognize that responses can vary.
AS is a complex condition with individualized symptoms and triggers.
Before making significant changes to diet or lifestyle, individuals with AS should consult their healthcare providers.
Some teas may interact with medications or have varying effects on different people, emphasizing the importance of personalized care.
Final Word
Tea, with its diverse range of types and flavors, has the potential to be more than just a beverage for individuals living with Ankylosing Spondylitis.
The anti-inflammatory properties of certain teas, coupled with the soothing nature of warm beverages, make tea an intriguing addition to the lifestyle of those managing AS.
Whether it’s the antioxidants in green tea, the pain-relieving properties of ginger and turmeric teas, or the overall ritualistic comfort of a warm cup, tea may play a supportive role in the holistic management of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
However, individuals must approach dietary changes mindfully, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals to ensure that incorporating tea aligns with their unique health needs and treatment plans.
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
Itsnevernotteatime.com cannot and does not contain medical/health advice. The medical/health information is provided for general and educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional advice.




